Abstract
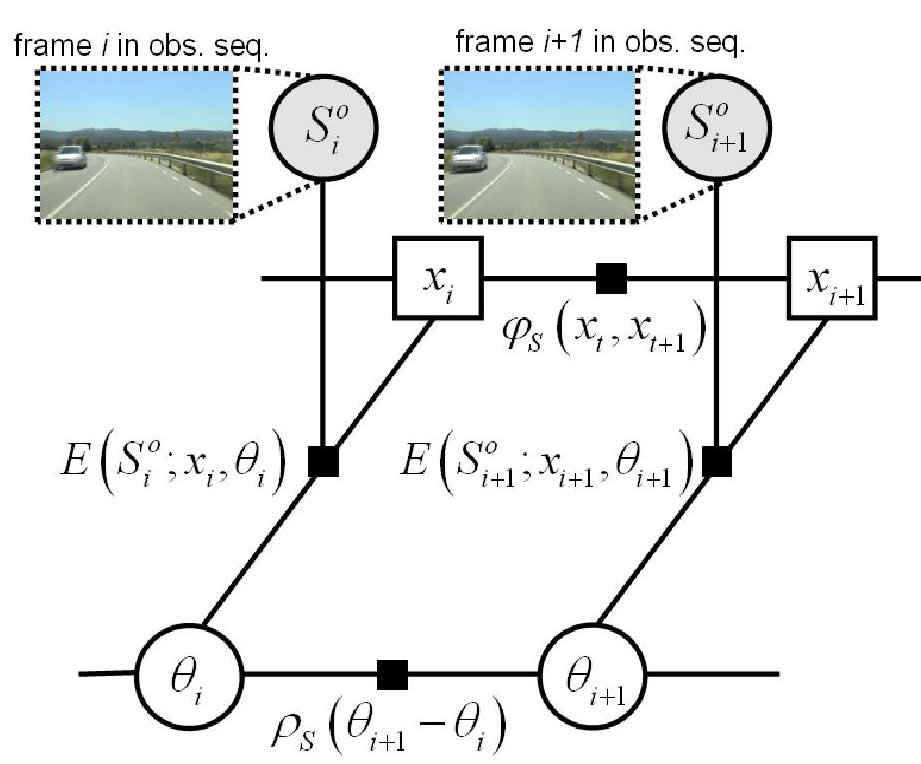
In this chapter, we propose a joint spatio-temporal video alignment to handle the most general problem and include the 'classic' case of fixed geometric transformation and/or linear temporal mapping as a particular case. In particular, the video alignment is formulated as a unique inference problem on a huge number of parameters, a non-parametric temporal correspondence and non-fixed geometric transformation, instead of tackling independently either temporal or spatial alignment. This simultaneously satisfies a frame-correspondence, or synchronization, and a frame-alignment, or image registration, along the whole sequence. Hence, this joint similarity accurately discriminates among successive frames that share a large similarity of content; thus reducing spatio-- and temporal--misalignments. This reduction is reinforced by exploiting the similarities between neighbor frames. The way we do it is by integrating the estimation of the spatio--temporal parameters into a standard pairwise Markov random filed (MRF); thus restricting the frame correspondence and spatial transformation according to the neighborhood. |
|
Sequences
Experiments are conducted on different video sequence pairs covering all the alignment cases as shown the below table to validate the proposed algorithm.
| Cameras | Temporal Correspondence | |
Affine |
unknown |
|
Static |
Water [1] |
|
Moving |
Indoor-2 [3] |
|
Highway
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
Liu's method
[6] |
Campus
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
Liu's method
[6] |
Back-road
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
Liu's method
[6] |
Indoor-1
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
Sand and Teller [5] |
Dancing
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
Jump
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
Indoor-2
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
Water
| Observed Sequence |
Reference Sequence |
| Joint Video Alignment |
References
[1] Y. Caspi and M. Irani, "Spatio–temporal alignment of sequences," IEEE Trans. PAMI., vol. 24, no. 11, pp. 1409–1424, 2002. Available in: http://www.wisdom.weizmann.ac.il/~vision/VideoAnalysis/Demos/Seq2Seq/Seq2Seq.html
[2] L. Gorelick, M. Blank, E. Shechtman, M. Irani, and R. Basri, "Actions as space-time shapes," Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, vol. 29, no. 12, pp. 2247–2253, December 2007. Available in: www.wisdom.weizmann.ac.il/~vision/SpaceTimeActions.html
[3] P. Kelly, N. O'Connor, and A. Smeaton, "A framework for evaluating stereo-based pedestrian detection techniques," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 18, pp. 1163–1167, August 2008. Available in: http://www.cdvp.dcu.ie/datasets/pedestrian_detection/
[4] C. Rao, A. Gritai, M. Sha, and et al., "View–invariant alignment and matching of video sequences," in Proc. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2003, pp. 939– 945. Available in: http://server.cs.ucf.edu/~vision/projects/ ViewInvariance/ViewInvariance.html
[5] P. Sand and S. Teller, "Video matching," ACM Transactions on Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH), vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 592–599, 2004. Available in: http://rvsn.csail.mit.edu/vid-match/
[6] C. Liu, J. Yuen, and A. Torralba, "Sift flow: Dense correspondence across scenes and its applications," IEEE Trans. PAMI, vol. 99, 2010.