Aim
In recent years industries increasingly use laser welding units. The benefit of laser welding compared to other methods lies in the higher economic efficiency.
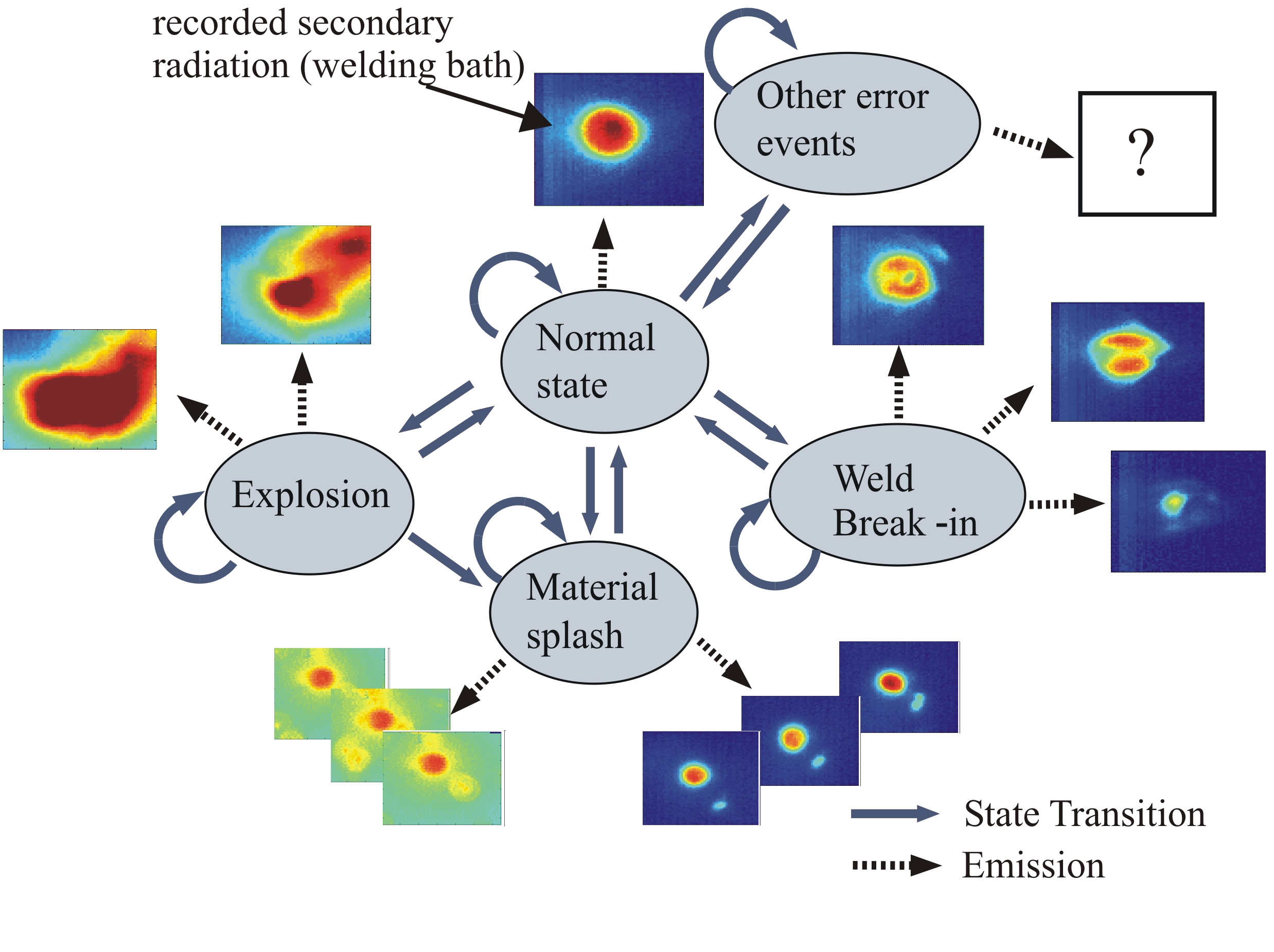
Industrial laser welding is a highly dynamical and chaotic process and thus vulnerable for process errors. Although process errors occur rarely, it is important to on-line monitor the process, to ensure that all faulty welds are detected. The aim of this study is to investigate classification strategies which allow a robust, automatic quality control of laser welding processes.
Methods
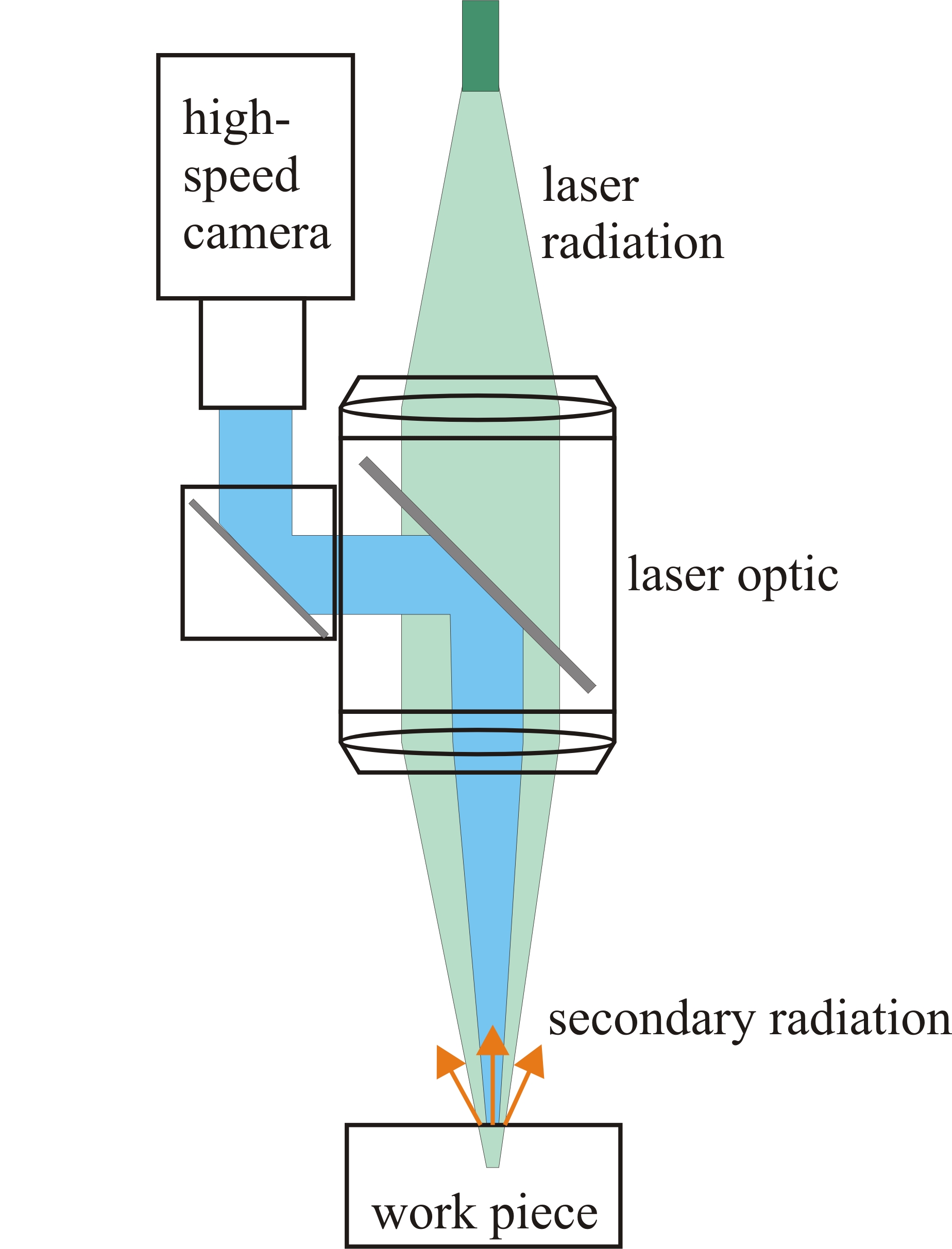
When laser radiation interacts with the work piece, secondary radiation is generated. This radiation contains information about the process stability and can thus be used to detect process errors.
The secondary radiation is recorded with one or several high speed CMOS cameras (with up to 40000 fps). Thus a high temporal correlation between the recorded frames is achieved. In state of the art laser welding process control systems the temporal dependencies are not fully exploited. Therefore we propose the use of Hidden Markov Models (HMM) to be able to model the temporal dependencies and increase the classification performance.