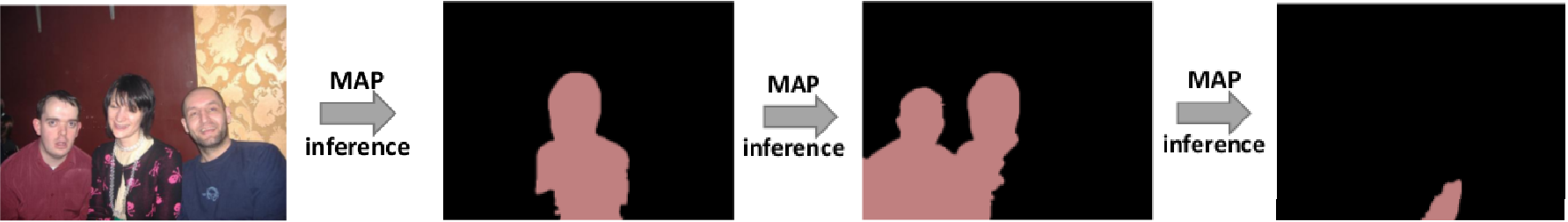
Motivation: In many application it is not sufficient to only compute the (approximate) MAP solution of a graphical model. Hence, Batra et al. proposed in ECCV 2012 the idea of computing multiple solutions with two criteria in mind: a) the solutions should have low energy; b) the solutions should be as different as possible (w.r.t. some diversity measure). Computing such “M-best diverse solutions” has since 2012 been used in many practical applications, e.g. to improve semantic segmentation. In our line of work on this topic we have improved inference techniques for computing “M-best diverse solutions” for different types of energies and different diversity measures. Our key insight has been that it is advantageous to compute the “M-best diverse solutions” jointly (see figures below).
Baseline Approach
Sequential inference of diverse labelings: D. Batra, P. Yadollahpour, A. Guzman-Rivera, and G. Shakhnarovich. Diverse M-Best Solutions in Markov Random Fields. ECCV, 2012. [paper]
Our Approach
Joint inference of diverse labelings as MAP-inference problem: [video spotlight]:
Our main results for node-wise diversities:
- Problem formulation and general algorithm: A. Kirillov, B. Savchynskyy, D. Schlesinger, D. Vetrov, C. Rother. Inferring M-Best Diverse Labelings in a Single One. [pdf with supplementary material][bib] [video spotlight] ICCV 2015
- Efficient algorithm for submodular energies: A. Kirillov, D. Schlesinger, D. Vetrov, C. Rother, B. Savchynskyy. M-Best-Diverse Labelings for Submodular Energies and Beyond. [pdf with supplementary material][bib] NIPS 2015
- Superefficient algorithm for binary submodular energies: A. Kirillov, A. Shekhovtsov, C. Rother, B. Savchynskyy. Joint M-Best-Diverse Labelings as a Parametric Submodular Minimization. [pdf][supplementary material] NIPS 2016